12 Which of the Following Lenses Is a Converging Lens
In the following figure F is the focus. A collimated laser beam of radius r 0 is incident upon a cylindrical plano-concave lens of focal length -f.

Imp Mnemonics And Optical Sign Conventions Mirrors And Lenses How To Study Physics Invert Image
The beam radius w lens at the lens must be small enough to avoid truncation or excessive spherical aberrations.

. They are also known as Double convex lenses. Concave lens is the lens that is thicker around the edges while the convex lens is the one with thick centres. The object is located in front of F for a converging lens.
Spherical lenses are mainly of two types. Parallel light strikes the diverging lens. 1F 1f 1 1f 2 df 1 f 1.
The perceived power of lenses changes as you change the distance between the lens and the eye Now as we know the lenses in glasses are at a different distance from the eyes than contact lenses are. Converging These are Lenses where light rays parallel to the optic axis pass through and converge together at a common point behind them. This falls into the category of Case 5.
The same reasoning applies to the diverging lenses as shown in part b. The third sample problem will pertain to a diverging lens. Lenses are the optical tools that have the ability to converge or diverge a beam of light through the process of refraction.
The laser beam will appear to be expanding from a virtual source placed a distance f. Typically it will be of the order of half the aperture radius of. I Which one of the two lenses you will select to use as the objective lens and why.
The resulting superlens resolved a silicon sample also having 50nm lines and spaces far beyond the. After passing through the converging lens the light is again parallel. Ii What should be the change in the distance between the lenses to have the telescope in its normal adjustment position.
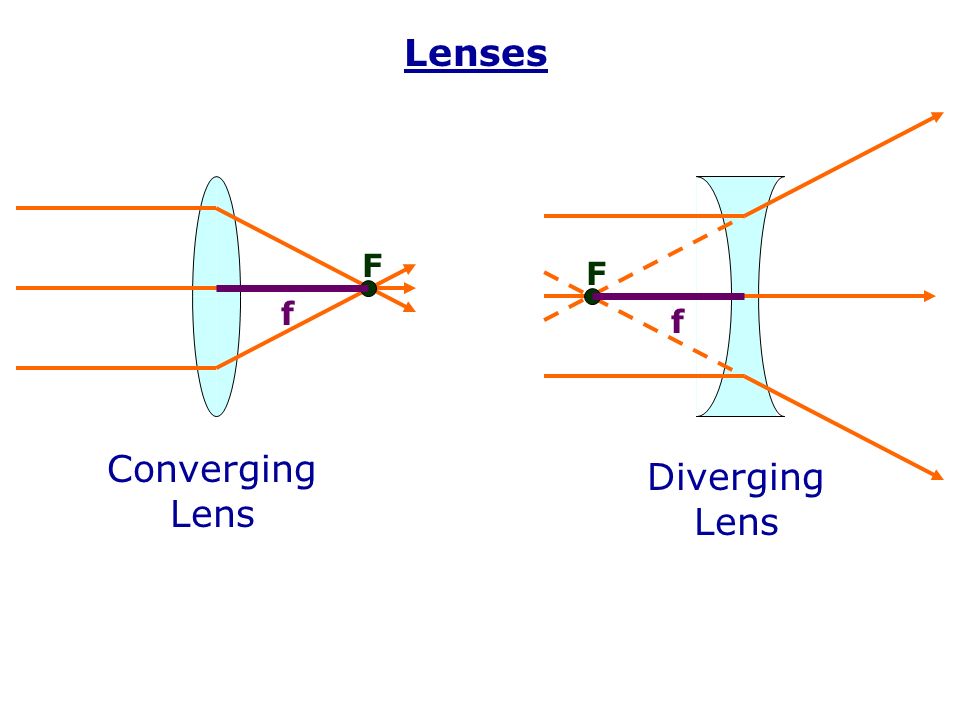
If the image distance is calculated to be negative it implies that the image formed is virtual and on the same side as the object. A ray that enters a diverging lens by heading toward the focal point on the opposite side exits parallel to the axis. In a convex lens the parallel rays of light passing through the lens actually meet at a point in front of the lens known as focus.
The focal length f of a converging lens is considered positive and that of a diverging lens is considered negative. A converging lens is wider in the middle than it is at the edges like a magnifying glass A diverging lens is wider at the edges than it is in the middle like a bowl. A common application of cylindrical lenses is shown in Figure 1.
For a diverging lens the point. A convex lens is also called a converging lens while a concave lens is known as a diverging lens due to its ability to converge and diverge. For thin lenses in contact it is pretty clear that the combined power of the system is given by adding the powers of the individual lenses.
Iii Calculate the magnifying power of. Sample Problem 3 A 400-cm tall light bulb is placed a distance of 355 cm from a diverging lens having a focal length of -122 cm. This point is.
Since the power is the reciprocal of the focal length what is very evident in this case. Two Types of Thin Lens. Power of the combination P P 1 P 2 ii When lenses are separated by a distance d.
If the focal length is negative it implies that the lens is concave diverging while if positive it implies that the lens is convex converging lenses. F 1 is the focal length of the first lens. Some lenses are used for focusing collimated laser beams to small spots.
Lens Formula in Terms of Power Image will be uploaded soon Fig1 shows two lenses L 1 and L 2 placed in contact. A 264 cm focal length converging lens is 164 cm behind a diverging lens. Power of the combination P P 1.
The numerical aperture of such a lens depends on its aperture and focal length just as for the collimation lens discussed above. These lenses bulge outward from both. The overall effect is that light rays are bent toward the optical axis for a converging lens and away from the optical axis for diverging lenses.
Where f is the combined focal length. Thus the power of a converging lens is positive and that of the diverging lens is negative. This is the Lens equation for Convex Lenses.
In this figure the radius of the laser beam is exaggerated for clarity. The laser beam will expand with a half-angle θ of r 0 f. Convex lens and concave lens.
Focal Length of a Lens Combination i When lenses are in contact 1F 1f 1 1f 2. Finding magnification is the same for both with one important exception. A ray entering a converging lens through its focal point exits parallel to its axis.
Consider an object some distance away from a converging lens as shown in Figure 1627. It consists of a spherical surface and a flat surface ie it bugles outward from one side and it has a plane surface on the other side. To find the location and size of the image formed we.
Click here to go straight to the diverging lens exception. The power of a convex converging lens is positive and for a concave diverging lens it is negative. To derive a thin Lens formula you must first understand that Lenses can be of two types converging and diverging.
In a nutshell this simple equation states that the perceived power of lenses changes as you change the distance between the lens and the eye. Determine the image distance and the image size. F 2 is the focal length of the second lens.
Convex lenses are broadly divided into the following categories. For a converging lens the point at which the rays cross is the focal point F of the lens. A superlens or super lens is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limitFor example in 1995 Guerra combined a transparent grating having 50nm lines and spaces the metamaterial with a conventional microscope immersion objective.
Two convex lenses A and B of an astronomical telescope having focal lengths 5 cm and 20 cm respectively are arranged as shown in Fig. Types of Convex Lens.

Physics Optics Lenses Converging Lens 3 Physics Optical General Physics
Lenses Converging Lens Diverging Lens F F F F Ppt Video Online Download

Which Type Of A Lens Is A A Converging Lens And Which Is B A Diverging Lens Explain Your Answer With Diagrams

No comments for "12 Which of the Following Lenses Is a Converging Lens"
Post a Comment